Heartworms threaten our beloved canine companions, lurking within their bodies and wreaking havoc on their health. Like silent assassins, these parasitic worms invade the hearts and lungs of dogs, causing severe damage and even death if left untreated. Understanding how dogs acquire heartworms is crucial in preventing this debilitating condition.
Imagine a delicate dance between two unsuspecting partners: the mosquito, a tiny buzzing creature seeking sustenance, and the dog, an innocent soul longing for companionship. In this intricate choreography of nature’s elements, mosquitoes are vectors for heartworm transmission. As they feed on infected animals, these blood-sucking insects become carriers of microscopic larvae that develop into mature heartworms within their bodies.
Dogs unwittingly become hosts to these insidious parasites through seemingly harmless mosquito bites. Once inside a dog’s body, the larvae journey through its bloodstream until they reach the heart and lungs—ideal breeding grounds for their growth and reproduction.
In this article, we will explore the life cycle of heartworms and how dogs become infected. We will also discuss common symptoms of heartworm infection in dogs, diagnostic testing methods available for early detection, prevention strategies to safeguard our furry friends’ well-being, and the risks and complications associated with this disease. By embracing responsible pet ownership practices and understanding the mechanisms behind heartworm transmission, we can protect our loyal companions from this difficult affliction.
Key Takeaways
- Mosquitoes are the primary vectors for heartworm transmission in dogs.
- Dogs become hosts to heartworms through mosquito bites.
- Larvae travel through the bloodstream to the heart and lungs, developing into mature worms.
- Preventive measures, such as administering monthly medications and controlling mosquitoes, are crucial for protecting dogs from heartworm infection.
The Life Cycle of Heartworms
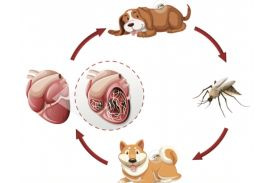
The life cycle of heartworms involves several stages, including transmitting microscopic larvae through mosquito bites to susceptible hosts. Understanding heartworm transmission is crucial for preventing and treating this potentially fatal disease in dogs.
Mosquitoes become infected with heartworm larvae by feeding on blood from an infected animal. Inside the mosquito, these larvae develop into infective forms that can be transmitted to a new host during subsequent blood meals.
When a mosquito carrying infective larvae bites a dog, the larvae are deposited onto the skin and enter the body through the bite wound. From there, they travel through the bloodstream and eventually settle in the pulmonary arteries and right side of the heart, where they mature into adult worms.
This complex life cycle highlights the importance of controlling mosquitoes and administering preventive medications to protect dogs from acquiring heartworm infections.
Mosquitoes as Vectors for Heartworm Transmission
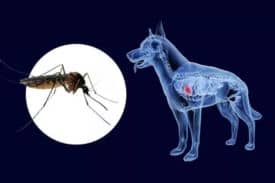
As tiny disease agents, mosquitoes play a pivotal role in the intricate web of heartworm transmission. Understanding how mosquitoes transmit heartworms is crucial for effective prevention and control strategies. Here are four key points to consider:
- Mosquitoes act as intermediaries: When a mosquito bites an infected dog, it ingests microscopic larvae called microfilariae and the blood meal.
- Development within the mosquito: Inside the mosquito, these microfilariae undergo further action over 10 to 14 days.
- Transmission through bite: Infective larvae migrate to the mosquito’s mouthparts after maturation. When this mosquito bites another susceptible dog, it injects these larvae into the new host’s bloodstream.
- Heartworm prevention: Effective heartworm prevention involves interrupting this transmission cycle by eliminating or reducing mosquitoes’ access to dogs through various methods such as insecticides and environmental management.
We can protect our canine companions from this potentially deadly disease by understanding mosquitoes’ role in heartworm transmission and implementing appropriate mosquito control and prevention measures.
How Dogs Get Infected with Heartworms
Heartworm infection in dogs occurs when they are exposed to infected mosquitoes outdoors. Mosquitoes serve as vectors for transmitting the heartworm larvae, which enter the dog’s bloodstream through a mosquito bite.
Additionally, dogs can become infected if preventive measures such as heartworm medications or mosquito control methods are not implemented consistently.
Outdoor Exposure to Mosquitoes
Outdoor exposure to mosquitoes is a significant risk factor for the transmission of heartworms in dogs. Mosquitoes serve as intermediate hosts for heartworm larvae (microfilariae), which are injected into the dog’s bloodstream during a mosquito bite. When infected mosquitoes feed on an infected animal, they ingest microfilariae. These microfilariae then develop into infective larvae within the mosquito over 10 to 30 days. Subsequently, when these infected mosquitoes bite another dog, they transmit the infective larvae into its bloodstream.
To reduce the risk of heartworm infection, it is essential to implement effective mosquito control measures and preventive strategies. This includes eliminating standing water sources where mosquitoes breed, using insecticide-treated bed nets or screens to prevent mosquito bites, and regularly administering preventive medications recommended by veterinarians. By implementing such measures, pet owners can greatly reduce their dog’s chances of acquiring heartworm disease and ensure their well-being.
| Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
| Eliminating standing water sources | Preventing mosquito breeding |
| Using insecticide-treated bed nets or screens | Protection from mosquito bites |
| Regular administration of preventive medications | Reducing the risk of heartworm infection |
Table: Mosquito Control and Heartworm Prevention Measures
Lack of Preventive Measures
Despite the wealth of information available on preventive measures, it is disheartening to see a lack of implementation in protecting canines from the devastating consequences of heartworm infection. This negligence is particularly concerning considering the range of effective and readily accessible methods for heartworm prevention in dogs. To highlight this issue, here are three crucial points to consider:
- Dog Heartworm Medication: Numerous medications are available that effectively prevent heartworm infection in dogs. These medications come in various forms, such as pills, topical applications, and injections, making them easy to administer.
- Regular Testing: Annual heartworm testing allows for early detection and timely intervention if necessary. This ensures that infected dogs receive appropriate treatment promptly, preventing further complications.
- Environmental Control: Apart from medication, implementing environmental control measures is vital in reducing mosquito populations and minimizing the risk of heartworm transmission.
By consistently adhering to these dog heartworm prevention methods, individuals can significantly reduce their beloved pets’ susceptibility to this potentially fatal disease while serving their well-being dutifully.
Common Symptoms of Heartworm Infection in Dogs

One of the key signs that a dog may be infected with heartworms is a persistent cough. This symptom occurs due to damage caused by the worms in the lungs and airways.
Additionally, infected dogs may experience fatigue, weight loss, and difficulty breathing. Dog owners need to recognize these symptoms as they can indicate a severe health issue.
Heartworm infection can harm a dog’s overall health if left untreated. If diagnosed with heartworm disease, common treatment options include medications to kill adult worms and prevent further larvae growth. However, treatment can be costly, requiring strict rest and limited physical activity for several weeks or months.
Therefore, owners must prioritize preventive measures such as regular testing and administration of preventives to protect their pets from this potentially life-threatening condition.
Diagnostic Testing for Heartworms
Heartworm infection can be accurately diagnosed through various diagnostic testing methods. These techniques are crucial for identifying the presence of heartworms in dogs, allowing for prompt treatment and minimizing the risk of complications.
Diagnostic techniques commonly used for heartworm detection include:
- Antigen Testing: This method detects specific proteins produced by adult female heartworms and is highly accurate.
- Microscopic Examination: A blood sample is examined under a microscope to identify microfilariae (immature heartworm larvae).
- Radiography: X-rays can reveal changes in the size and shape of the heart and lungs, indicating the presence of adult worms.
- Ultrasound: This imaging technique allows veterinarians to visualize adult heartworms within the dog’s heart and pulmonary arteries.
Once diagnosed, treatment options for canine heartworm infection may involve medication to kill adult worms or surgery for severe cases that require worm removal. It is essential to consult a veterinarian to determine the most appropriate approach based on individual circumstances.
Treatment Options for Heartworm Disease
Treatment options for heartworm disease include medication to eliminate adult worms and surgical procedures for severe cases requiring worm removal. The primary goal of treatment is to kill adult worms, which can take several months.
Medications commonly used include melarsomine dihydrochloride, which is administered by injection. This drug kills adult worms and is typically given several injections over time.
In addition to medication, it is also important to implement heartworm prevention measures to prevent future infections. Preventive options include monthly administration of drugs such as ivermectin or milbemycin oxime, which kill the immature larvae before they can develop into adult worms.
Regular screening and continued preventive measures are essential in managing heartworm disease and reducing the risk of infection in dogs.
Prevention Strategies for Heartworms
Implementing effective prevention strategies is crucial in safeguarding against the transmission and establishment of heartworm disease, as these measures act as a shield, fortifying the overall well-being of our beloved furry companions. To effectively prevent heartworms, consider the following tips:
- Administer preventive medication: Regularly provide your dog with veterinarian-recommended heartworm preventative medication to kill any larvae that may have been transmitted.
- Avoid mosquito bites: Minimize your dog’s exposure to mosquitoes by keeping them indoors during peak mosquito activity times and using appropriate insect repellents.
- Eliminate mosquito breeding grounds: Remove standing water sources such as stagnant ponds or puddles to reduce mosquito populations in your surroundings.
- Annual testing: Schedule heartworm tests for early detection and prompt treatment if necessary.
Adhering to these prevention strategies can significantly reduce the risk of your dog contracting heartworm disease and ensure their long-lasting health and happiness.
Importance of Annual Heartworm Testing
Annual heartworm testing plays a critical role in monitoring and managing the health of our canine companions, as it allows for early identification of heartworm infection and facilitates prompt intervention to prevent further complications.
Annual heartworm prevention is essential in safeguarding dogs against this potentially fatal disease. While preventive measures are effective, there is still a possibility that dogs may contract heartworms despite being on preventative medication. This makes annual testing crucial as it helps detect the presence of heartworms early before clinical signs become apparent. Early detection enables veterinarians to initiate appropriate treatment promptly, preventing the progression of the disease and minimizing potential damage to the dog’s cardiovascular system.
Moreover, annual testing ensures that preventative medications are working effectively and provides an opportunity to discuss any concerns or questions regarding heartworm prevention with veterinary professionals.
By prioritizing annual heartworm testing, dog owners can ensure their pets receive optimal care and protection from this serious parasitic infection.
Risks and Complications of Heartworm Infection
Heartworm infection in dogs can lead to risks and complications that can significantly impact their health. Adult heartworms in the heart and lungs cause damage to these vital organs, leading to respiratory problems and cardiovascular dysfunction.
Additionally, as the worms reproduce, they release microfilariae into the bloodstream, further blocking blood vessels and causing inflammation. If left untreated, this can result in symptoms such as coughing, fatigue, weight loss, and even heart failure.
The risks and complications associated with heartworm infection highlight the importance of preventive measures such as annual testing and regular administration of preventative medications. By identifying disorders early on, veterinarians can implement appropriate treatment plans to minimize the impact of this potentially life-threatening condition.
Therefore, dog owners must prioritize regular heartworm testing so their furry companions receive the necessary care and protection against these risks.
3 Complications Associated with Heartworm Infection:
- Respiratory problems caused by blockage of blood vessels
- Cardiovascular dysfunction due to damage to the heart
- Increased risk of heart failure if left untreated
The Role of Responsible Pet Ownership in Heartworm Prevention
Responsible pet ownership plays a pivotal role in the prevention of heartworm infection, ensuring the well-being and longevity of our beloved canine companions.
One key aspect of responsible pet ownership is managing outdoor activities carefully. Dogs are more likely to come into contact with mosquitoes, which are carriers of heartworm larvae when they spend time outdoors. By reducing mosquito exposure, owners can significantly decrease the risk of their dogs contracting heartworms.
This can be achieved by limiting outdoor activities during peak mosquito times, such as dusk and dawn, or using protective measures like insect repellents specifically formulated for dogs. Additionally, creating a safe and secure outdoor environment for pets can help minimize their contact with mosquitoes and reduce the chances of heartworm transmission.
By practicing responsible pet ownership and taking necessary precautions during outdoor activities, dog owners can prevent heartworm infections in their furry friends.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can heartworms be transmitted to humans?
Heartworms cannot be transmitted to humans. They are primarily transmitted through mosquito bites and only affect dogs, cats, and other animals. Prevention methods for dogs include regular heartworm medication and avoiding exposure to mosquitoes.
Can heartworms be transmitted through direct contact with an infected dog?
Heartworms cannot be transmitted through direct contact with an infected dog. Transmission occurs through the bite of a mosquito carrying heartworm larvae. However, transmission through saliva or shared toys is not a known mode of communication for heartworms.
Can heartworms be transmitted through other insects besides mosquitoes?
Heartworms cannot be transmitted through fleas or ticks. The primary mode of transmission is through mosquitoes. It is important to prevent dog heartworm infection using mosquito control measures and regular preventive medication.
Can heartworms be transmitted through blood transfusions?
Heartworms cannot be transmitted through blood transfusions or organ transplants. The primary mode of transmission is through the bite of infected mosquitoes. Other insects, such as fleas or ticks, do not significantly affect heartworm transmission.
Can heartworms be transmitted through mating or breeding?
Heartworms cannot be transmitted through mating or breeding. The transmission of heartworm disease occurs through the bite of infected mosquitoes. Therefore, taking precautions such as using preventive medications and regular veterinary check-ups is important to protect dogs from this disease.
Conclusion
In conclusion, heartworms can present a fatal threat to our beloved canine friends, yet understanding how they are transmitted and acting preventively can ensure a happy, heartworm-free life for them.
Here at Bone Voyage Dog Rescue, we have countless dogs, all heartworm-tested and given the necessary preventative care, eagerly awaiting a forever home.
By choosing to adopt from us, you gain a loyal companion and contribute to the fight against heartworms by providing a safe environment for a rescued dog. Together, we can lower the number of cases and ensure that heartworms never steal another dog’s joy.
Ready to embark on this voyage with us? Navigate to our adoption page today, and let’s make a difference, one dog heart at a time. Remember, every heart matters, especially those beating in the chest of a loving, furry friend.
